How Does a Turbocharger Work?
How Does a Turbocharger Work?
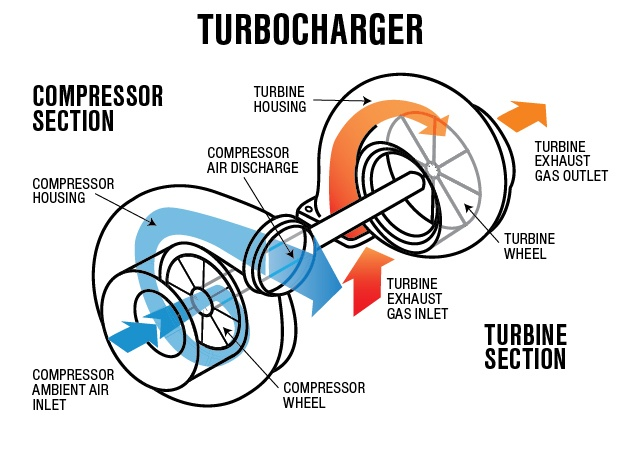
While a turbocharger uses wasted exhaust gases to produce more power, Turbochargers operate off a different part of the engine. Turbocharger s are powered mechanically by the belt or chain that goes to the crankshaft. They force more air into the engine so that more fuel can be burned, which in turn creates more energy. Turbocharger increase air intake by compressing the air above atmospheric pressure.
A Turbocharger draws its power directly from the crankshaft. Most of them use an accessory belt, which is wrapped around a pulley that is connected to a drive gear. Once the drive gear rotates, it rotates the compressor gear. The compressors job is to draw in more air and squeeze it into a smaller space. This is then discharged into the intake manifold.
Meanwhile, the turbine powers an air compressor, which gathers cold, clean air from a vent and compresses it to 30 percent above atmospheric pressure, or nearly 19 pounds per square inch. Dense, oxygen-rich air flows to the combustion chamber.
Turbochargers also improve the fuel efficiency of a vehicle however there is a misconception when it comes to turbocharged vehicles and fuel efficiency. Taking a naturally aspirated engine and slapping on a turbocharger on it will not improve fuel efficiency. The way that manufacturers improve fuel efficiency though turbocharging is by down-sizing an engine and then turbocharging it. For example, take a 2.5L inline-4 cylinder naturally aspirated engine and decrease the displacement to 1.4L and then turbocharger it. The smaller, turbocharged engine would still have the same performance figures (or slightly better) but because of the smaller displacement, it would also use less fuel.