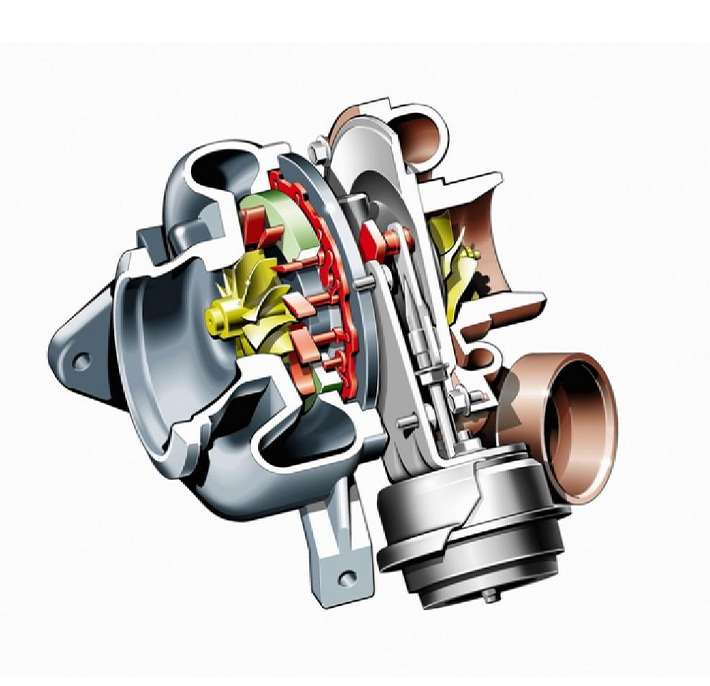
In the same contact with high-temperature gas, why can the turbocharger be burned red and the piston can hold it?
In the same contact with high-temperature gas, why can the turbo charger be burned red and the piston can hold it?
The temperature of the turbo charger is very high, because it is driven by the exhaust gas of the engine, especially when some engines have a large throttle during the test, the turbo charger can burn red. Here comes the question: Pistons are also exposed to the heat of engine combustion when they are working. Why don't you see the pistons being burnt red? There are mainly the following reasons:
1. Pistons aren’t constantly exposed to high temperatures
Only work stroke, exhaust stroke piston will contact with high-temperature gas, intake and compression stroke piston contact is the mixture of new inhalation. And as the intake stroke enters the cylinder, some of the heat is absorbed by the gas as it is vaporized, while the turbo charger is continuously heated, so the more heat is absorbed, the higher the temperature.
2. The difference between the contact area with high temperature gas
Only the upper surface of the piston is in contact with the high-temperature gas, and not all the gas is in contact. Especially when the piston moves to the bottom dead center, the volume of the high-temperature gas increases, and the actual gas in contact with the piston is even less. The high-temperature gas flows from the inside of the turbo charger, and has a wider contact area with the turbo charger shell, and all the gas passes through the turbo charger, which naturally transfers more heat to the turbo charger.
3. The piston has cooling
There is an oil nozzle under the piston of most engines to spray oil into the piston. This oil can take away part of the heat of the piston. Although the turbo charger also has cooling, the coolant and oil are cooled at the same time, but the core of the cooling is to increase The vicinity of the compressor turbine shaft is not to cool the entire turbo charger, which makes the turbo charger shell more likely to burn red when working under heavy load.
It can be seen that the piston actually bears a lower thermal load, and there is also oil and intake air for cooling. The inside of the turbo charger (especially the turbocharger housing) is almost continuously burned by the high-temperature exhaust gas, and there is no forced heat dissipation, so it is naturally more likely to be burnt red.